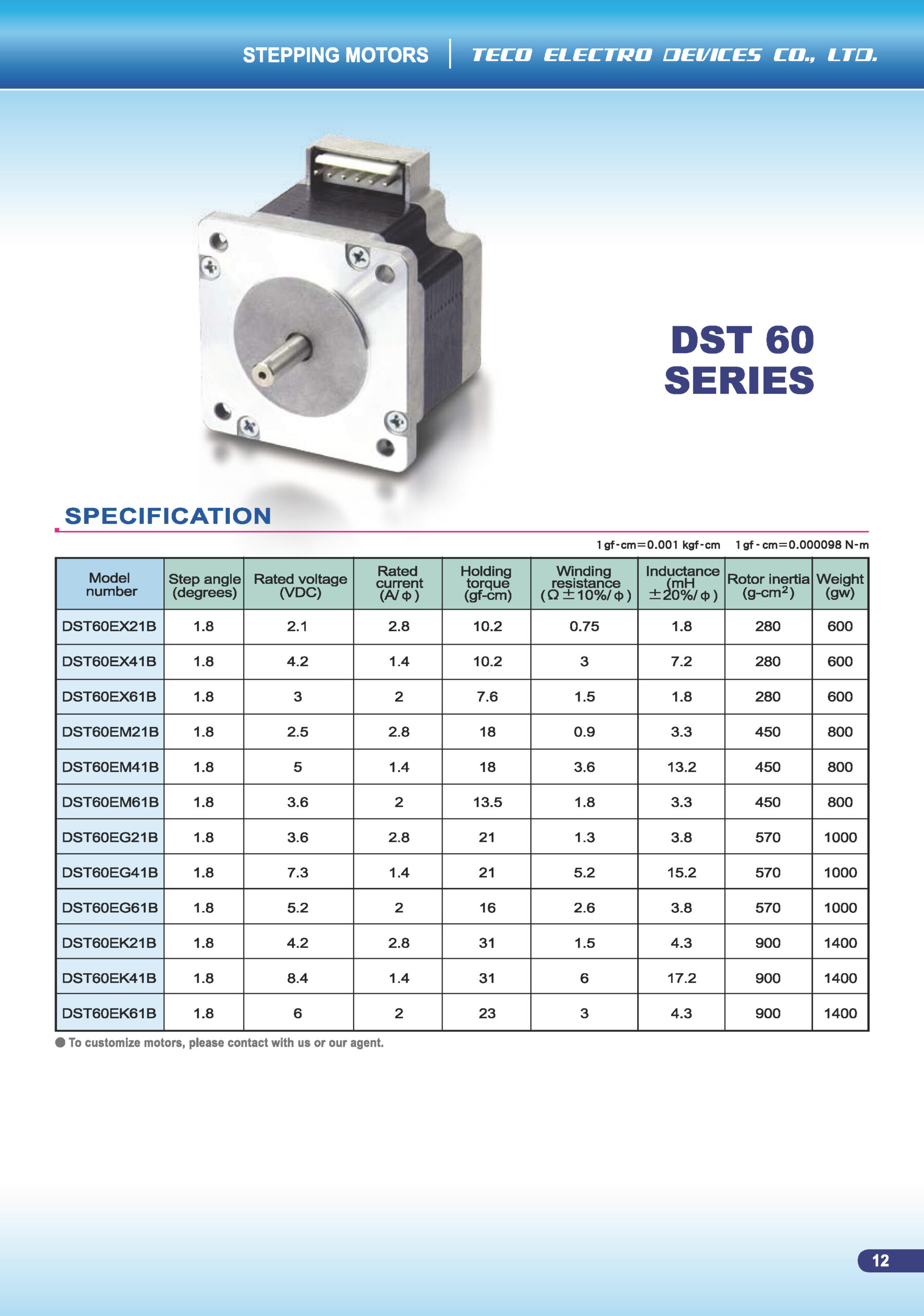
DST 60 Series Stepper Motor
The DST60 Series is part of TECO’s DST family of hybrid stepper motors. The “60” in the name denotes the frame size class (~60 mm).
The “Connector Series” designation means the motor includes a plug-in connector rather than loose leads, simplifying wiring and enabling more modular installation.
It is suited for applications that require moderate torque and incremental positioning, while benefiting from the convenience of connector wiring.
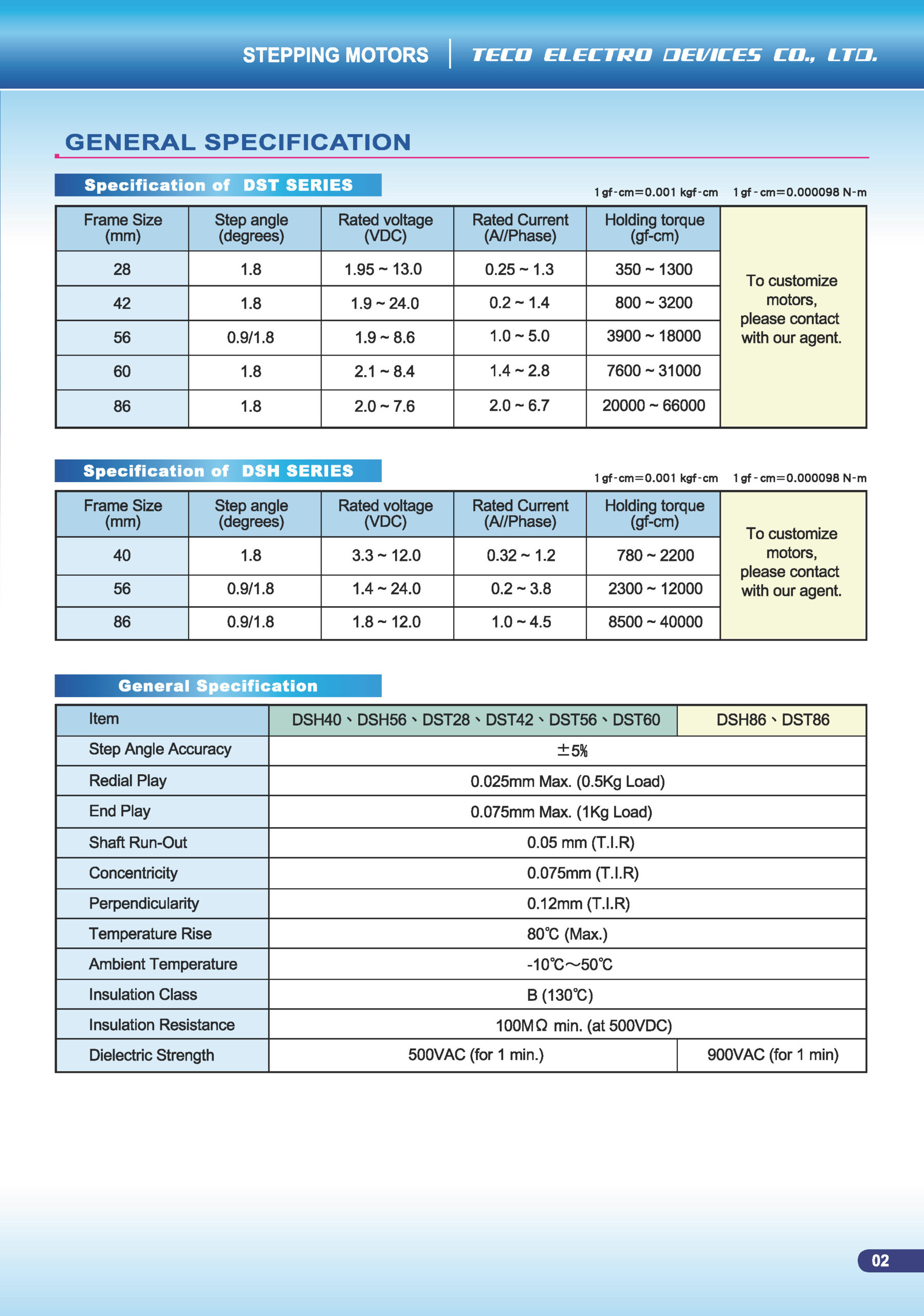
Key Features & Typical Specifications
Frame Size (~60 mm class): Larger than the smaller series (e.g., DST42, DST56) and offers higher torque capacity.
Connector Interface: Factory-fitted plug reduces wiring errors and simplifies maintenance.
Hybrid Stepper Design: Fixed step increments (common step angle is 1.8° per full step), ideal for precise positioning.
Electrical Parameters (example range from catalogue):
Winding Resistance: around 0.75 Ω to 6 Ω for the DST60 class.
Inductance: around 1.8 mH to 17.2 mH.
Rotor Inertia and Motor Weight: Example values: rotor inertia ~280 / 450 / 300 / 570 / 900 g-cm²; motor weight ~600 / 800 / 1000 / 1400 gW for DST60 size class.
Typical Applications
Indexing tables, rotary feeders, and small conveyors in packaging or automation systems.
Medium-torque positioning axes where stepping motion is sufficient and modular wiring benefits are essential.
Machine modules where open-loop step control is appropriate, and servo systems would be over-spec or too costly.
Design & Selection Considerations
Torque vs Speed: As with all stepper motors, available torque decreases at higher speeds — users should consult the specific DST60 torque vs. speed curves in the datasheet.
Inertia Matching: Ensure the load’s inertia is compatible with the motor’s rotor inertia to avoid lost steps or resonance.
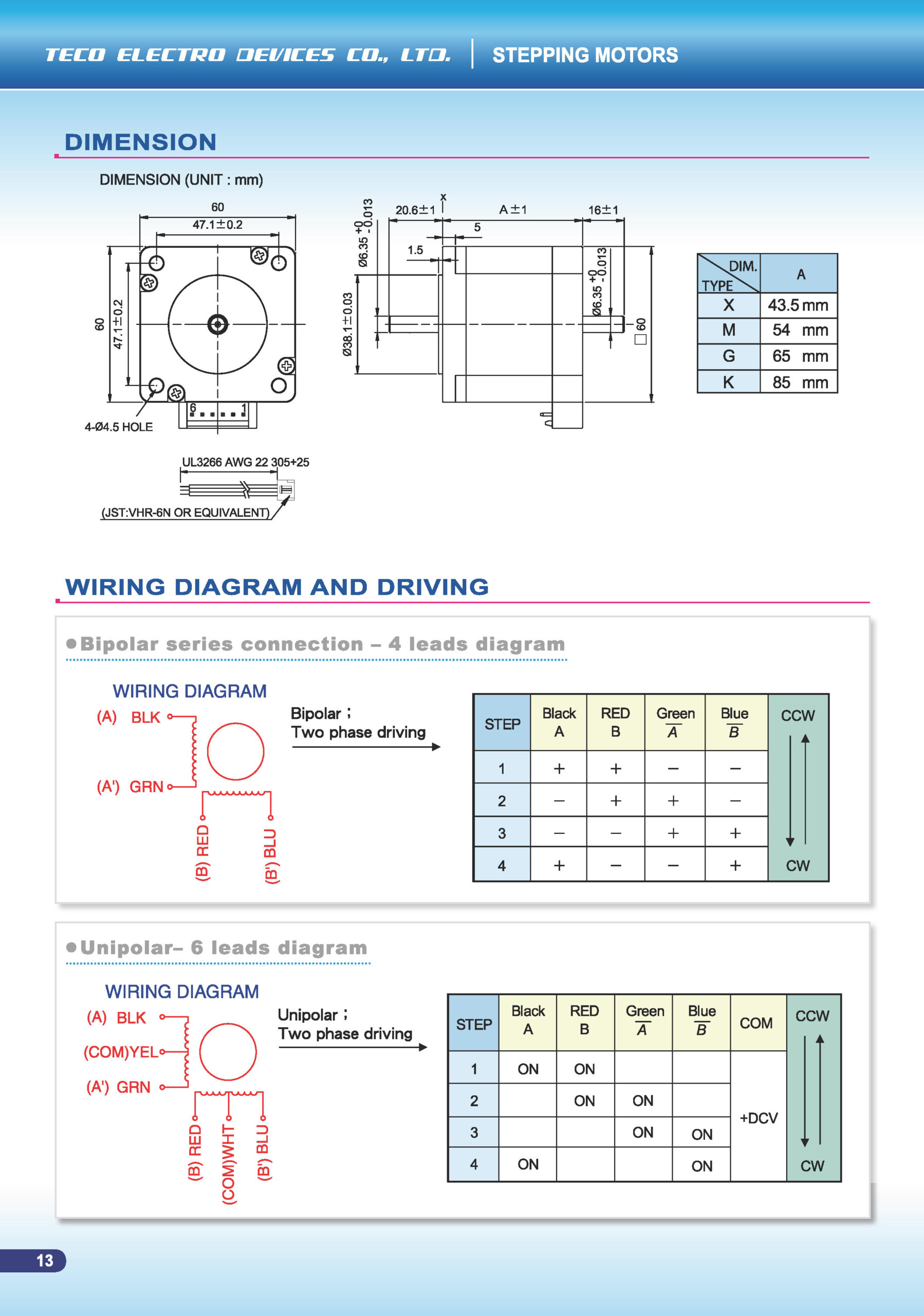
Driver & Wiring: The connector version requires a compatible stepper driver and correct cabling; confirm the connector pin-out, current rating, and wiring style (bipolar/unipolar) match your system.
Control Strategy: Open-loop control is common, but if high speed, high precision, or variable loads are involved, consider closed-loop stepper or servo alternatives.
Mechanical Integration: For a ~60 mm frame class, check mounting, shaft coupling, cooling, and wiring routing to ensure reliable operation.
The DST60 Series Stepper Motor from TECO offers a larger-frame stepper solution with a connector interface — combining higher torque capacity with modular wiring integration.
When properly selected for load inertia, driver compatibility, and control strategy, it provides a cost-efficient, reliable positioning motor for many automation tasks.